Hombre & Mujer
La NASA encontró moléculas de azúcar en antiguos meteoritos
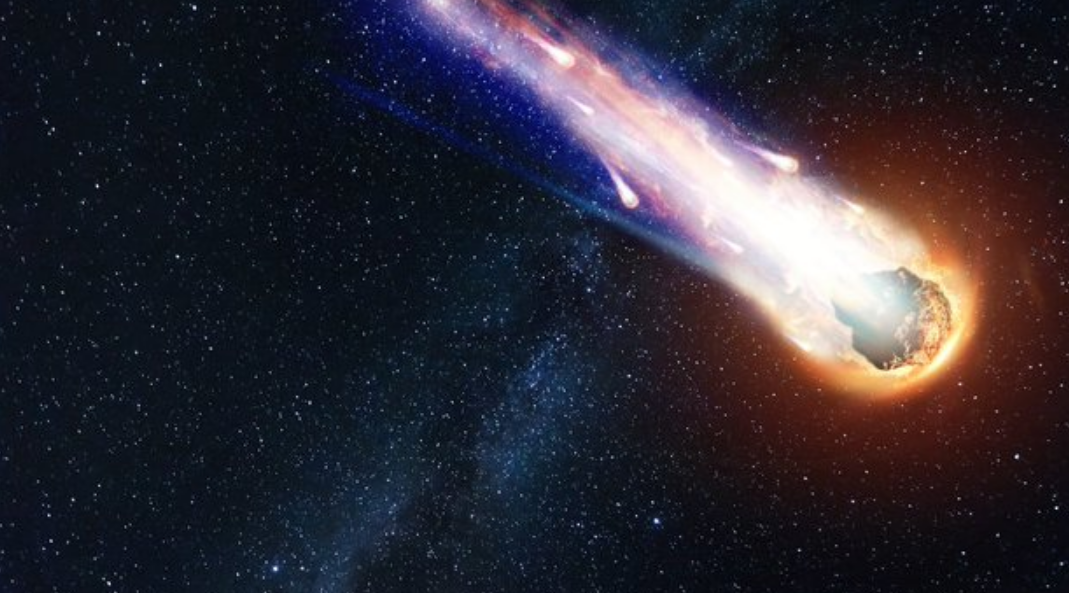

Meteoritos que se estrellaron en la Tierra hace billones de años contienen trazas de azúcar, según afirman los investigadores de la NASA, lo que respalda la idea de que los asteroides pueden contener algunos de los ingredientes esenciales para la vida.
Un equipo internacional de científicos encontró azúcares «bio-esenciales» en meteoritos, que también contienen otros compuestos biológicamente importantes, según un comunicado de prensa publicado por la NASA.
Los asteroides, objetos rocosos cercanos a la Tierra que orbitan alrededor del sol, son los cuerpos principales de la mayoría de los meteoritos. La teoría sugiere que las reacciones químicas dentro de los asteroides pueden crear algunos de los elementos esenciales para la vida.
En un estudio publicado en las Actas de la Academia Nacional de Ciencias, los investigadores analizaron tres meteoritos, incluido uno que aterrizó en Australia en 1969 y data de miles de millones de años.
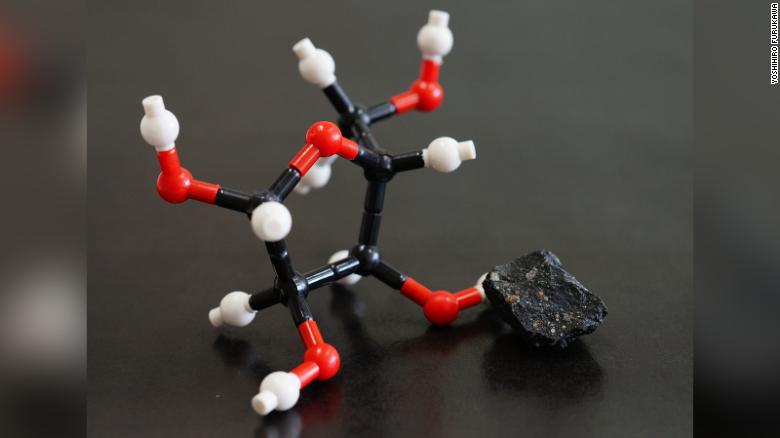

La NASA detectó la presencia de moléculas de azúcares en antiguos meteoritos. Foto: fuentes.
Presencia de azúcar en antiguos meteoritos
Estudios anteriores también han tratado de investigar los meteoritos para corroborar la presencia de azúcares; pero esta vez, los investigadores utilizaron un método de extracción diferente con ácido clorhídrico y agua.
Los investigadores encontraron azúcares como la arabinosa y la xilosa, pero el hallazgo más significativo fue la ribosa.
La ribosa, juega un papel muy importante en nuestra biología humana. Existe en nuestras moléculas de ARN (ácido ribonucleico) y entrega mensajes de nuestro ADN; para ayudar a construir proteínas para nuestros cuerpos, según el comunicado de prensa.
«Es notable que se pueda detectar una molécula tan frágil como la ribosa en un material tan antiguo»; dijo Jason Dworkin de la NASA, coautor del estudio, en el comunicado de prensa.
El descubrimiento de la ribosa también sugiere que el ARN evolucionó antes que el ADN; dando a los científicos una imagen más clara de cómo se pudo haber formado la vida.
NASA discovered sugar molecules in meteorites that crashed to Earth 30 years ago: NewsMic https://t.co/8wFAn3mBZ2 #space
— EcoInternet (@EcoInternetDrGB) November 25, 2019
Con información de: ACN|CNN|Redes
No dejes de leer: Misteriosa desaparición de una estación de datos marítima alemana
Hombre & Mujer
Tras aranceles de Trump, China registra cantidad récord de importación de crudo canadiense

China estaría registrando cantidades récords de importación de crudo canadiense, tras reducir drásticamente las compras de petróleo estadounidense, en medio de la ‘guerra’ arancelaria con Donald Trump.
La ampliación de un oleoducto en el oeste de Canadá, inaugurado hace menos de un año, ha brindado a China y a otros importadores de petróleo del este de Asia un mayor acceso a las vastas reservas de crudo de la región de arenas petrolíferas de Alberta.
Las importaciones chinas de crudo desde el puerto en la terminal del oleoducto cerca de Vancouver se dispararon a la cifra sin precedentes de 7.3 millones de barriles en marzo y van camino de superar esa cifra este mes, según datos de Vortexa, que rastrea los envíos de petróleo y gas natural por vía marítima.
Mientras tanto, las importaciones chinas de petróleo estadounidense se han desplomado a 3 millones de barriles mensuales desde un máximo de 29 millones en junio.
China importa más petróleo de Canadá
El cambio en los flujos de crudo norteamericano hacia China, el mayor importador de crudo del mundo, es otro ejemplo de las disrupciones económicas y estratégicas generadas por las medidas del presidente estadounidense Donald Trump para reestructurar las relaciones comerciales globales.
Para ser claros, el ‘apetito’ de China por el crudo canadiense comenzó a crecer cuando la expansión del oleoducto Trans Mountain, conocido como TMX, comenzó a transportar petróleo de Alberta a la costa del Pacífico de Columbia Británica en mayo.
La tendencia solo se aceleró después de que Trump asumiera el cargo con la intención declarada de imponer aranceles a China y otros países.
“Dada la ‘guerra’ comercial, es improbable que China importe más petróleo estadounidense”, declaró Wenran Jiang, presidente del Foro Canadá-China de Energía y Medio Ambiente, en una entrevista telefónica.
“No van a depender solo del petróleo ruso ni del de Oriente Medio. Cualquier producto canadiense será una buena noticia”, apuntó.
Aunque las importaciones chinas de petróleo de Norteamérica son insignificantes en comparación con las de Oriente Medio y Rusia, las arenas bituminosas canadienses constituyen una de las pocas fuentes de crudo relativamente barato, denso y con alto contenido de azufre, que muchas de las refinerías más avanzadas de China están equipadas para procesar
Para las refinerías asiáticas, el crudo de Oriente Medio con características similares, como el crudo pesado de Basrah de Irak, es caro en comparación con el petróleo de Alberta, dada la fortaleza del crudo de referencia de Dubái en la región.
Con información de: El Financiero
No dejes de leer: Así define el sexo biológico Supremo británico
Infórmate al instante únete a nuestros canales
WhatsApp ACN – Telegram NoticiasACN – Instagram acn.web – TikTok _agenciacn – X agenciacn
-

 Economía8 horas ago
Economía8 horas agoCámara de Comercio de La Guaira advierte que altos costos limitan actividad portuaria
-
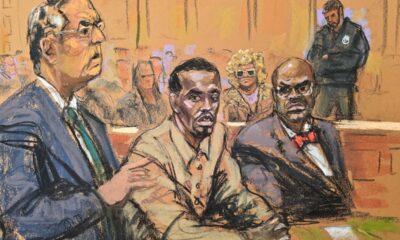
 Espectáculos12 horas ago
Espectáculos12 horas agoJuicio contra «Diddy» Combs declarado culpable de solo dos cargos (+ videos)
-

 Economía7 horas ago
Economía7 horas agoPagan «Bono Único Familiar» de julio con incremento
-

 Economía6 horas ago
Economía6 horas agoPrecio del dólar para 3 de julio y otras divisas por BCV























