Tecnología
¡Rodeado de misterio! gigantesco objeto apareció en un radar sobre México (+Video)
Reportaje Especial de ACN
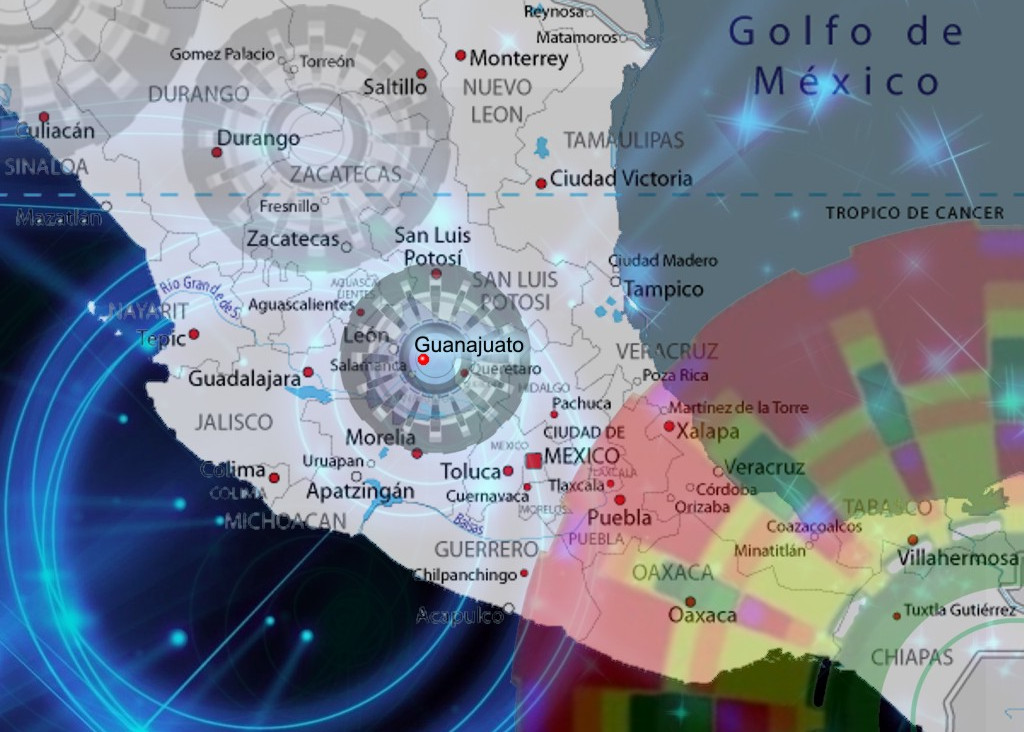
Esta semana, se ha vuelto viral en la redes un misterioso objeto que fue captado por sistemas de previsión meteorológica (radar), sobre la ciudad de Guanajuato (México) el pasado martes 1º de septiembre.
De acuerdo a la información que se ha compartido en internet por gran cantidad de usuarios, un gigantesco objeto de forma circular y de aspecto evidentemente “tecnológico”, fue captado al rededor de las 8:00 a.m. (hora local), del 1 de septiembre 2020 por una estación de radar doppler del servicio meteorológico nacional de México, permaneciendo visible en el sistema por mas de 30 minutos.
El misterioso objeto, apareció abarcando una extensión de casi 300 kilómetros, con su centro emplazado directamente sobre la localidad de “El Cubo”, ubicada a solo 10 kilómetros al sureste de Guanajuato. Como dato adicional, El Cubo posee una rica mina de oro y plata; que fue operada hasta el año pasado por la empresa canadiense Endeavour Silver.
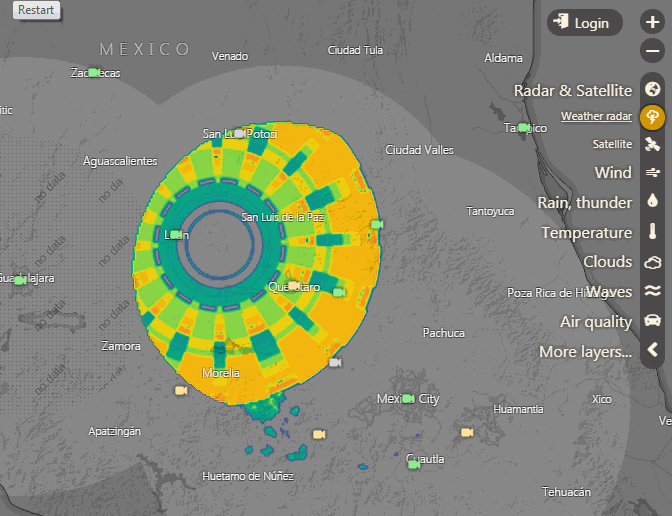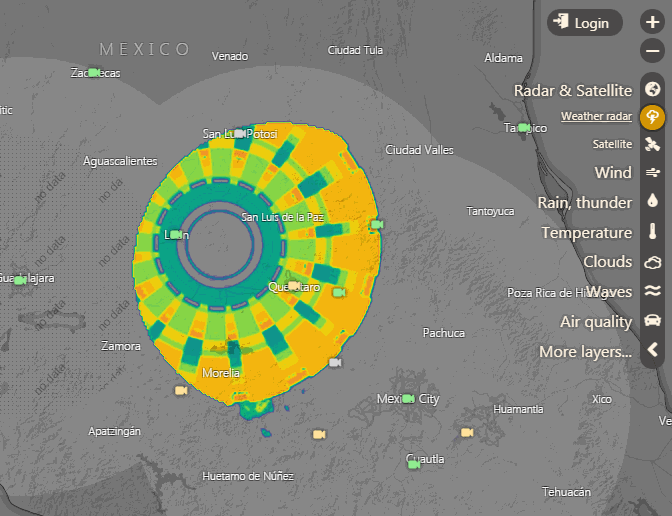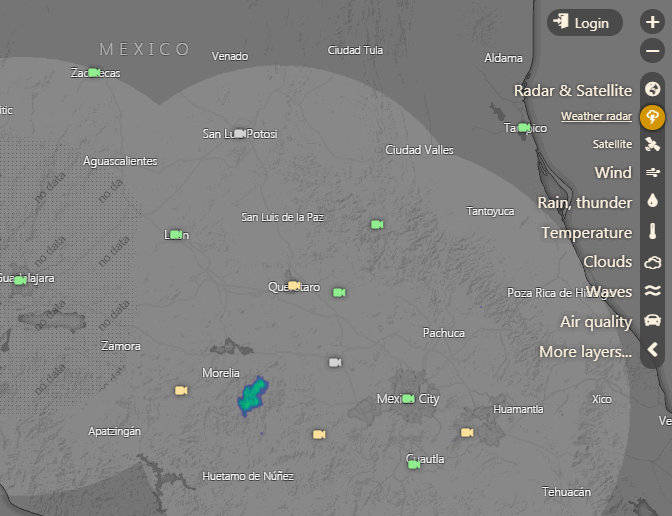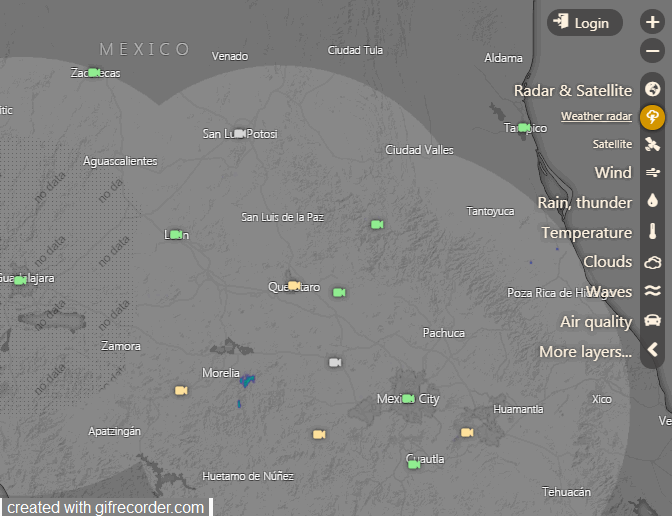
Animación de la imagen de radar captada el 1 de septiembre sobre Guanajuato. Gráficos cortesía de Windy.com
Detalles de la inmensa anomalía que apareció en el radar de México
La inmensa anomalía captada sobre Guanajuato, en ningún momento apareció en el rango visual de las imágenes enviadas por los satélites meteorológicos; pero si aparece en las imágenes de radar doppler de varios servicios climáticos entre los cuales destacan los portales: Windy, Open Weather y Ventusky entre otros.
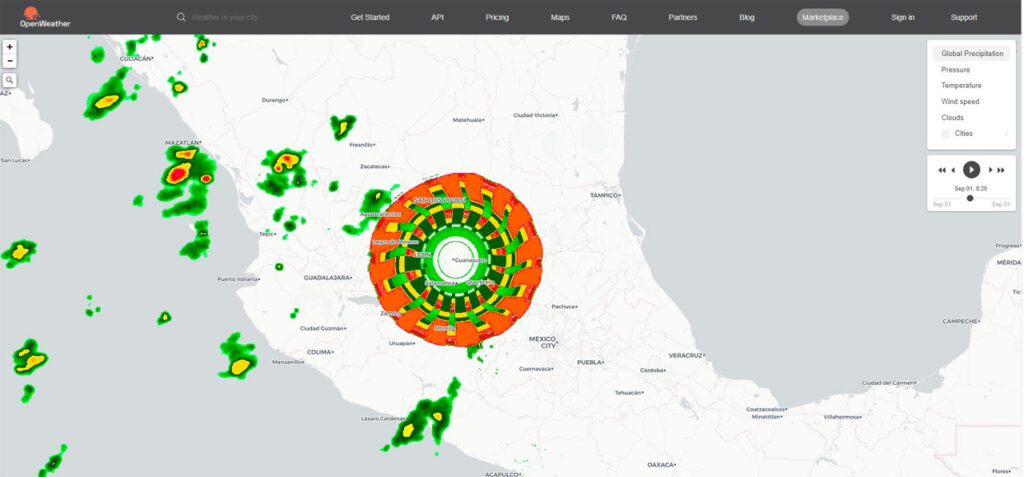
Imagen de radar del misterioso objeto captado sobre Guanajuato (México). Gráficos: Cortesía/ Open Weather.
Entre las teorías que se formularon inicialmente para intentar explicar el extraño fenómeno, algunos usuarios de las redes discutieron sobre un presunto mal funcionamiento del equipo de radar meteorológico emplazado en Guanajuato; pero esa teoría no explica porque los otros servicios de meteorología también captaron el fenómeno.
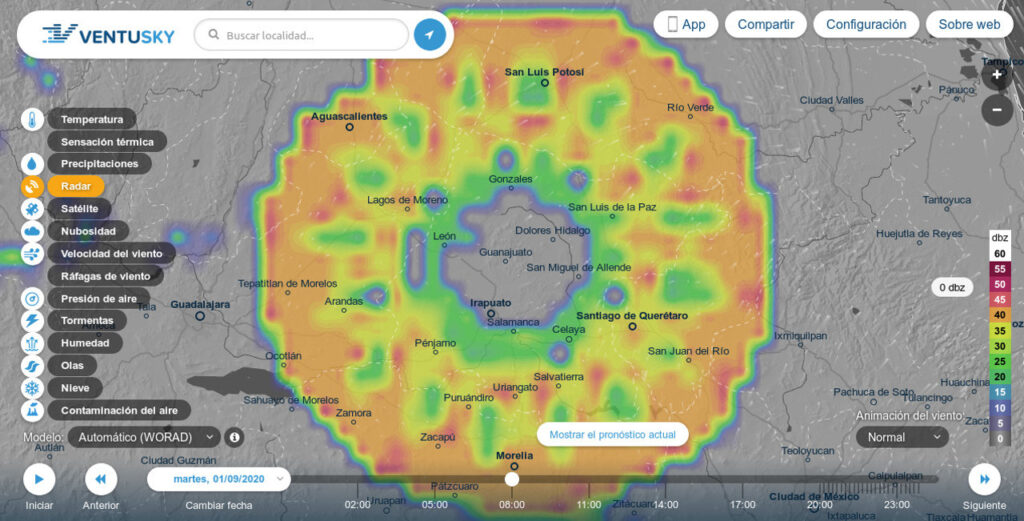
Imagen del enorme objeto captado en radar sobre Guanajuato. Gráficos: Cortesía/ Ventusky.com
El objeto, que apareció sobre el mapa mexicano abarcando un área de mas de 300 kilómetros, tiene forma de “rueda dentada” en su parte exterior, y posee un total de 16 estructuras similares a los rayos de las ruedas antiguas; que van desde el exterior hacia su centro, la mitad de los cuales es mas delgada que el resto y se encuentran distribuidos de forma intercalada.

Imagen vectorizada realizada siguiendo los patrones que se aprecian en las imágenes de radar de diferentes portales climáticos. Gráfico: ACN.
La misteriosa anomalía, también posee 16 estructuras mas gruesas con forma de “cuña”, cerca del borde exterior y entre las estructuras anteriormente mencionadas.
Así mismo, se sabe que el objeto captado por el radar doppler no es plano y es simétrico; lo cual acrecienta el misterio sobre su origen. La forma del objeto guarda similitudes de diseño con la conocida “Piedra del Sol” que es la base del antiguo calendario Azteca.

Piedra de Sol, exhibida en el Museo Nacional de Antropología e Historia de México y que se considera la base del Calendario Azteca. Foto: Cortesía/ Wikipedia.
Teorías en torno al origen de la extraña anomalía de radar en Guanajuato
Como era de esperarse, la información causó gran controversia en las redes, misma que no ha hecho sino crecer tras el paso de las horas; cuando cada momento parece aportar nuevos datos al misterioso asunto.
Recientemente, se supo que usuarios mexicanos lograron ubicar anomalías similares en fechas tan lejanas como el 2012; no solo sobre Guanajuato sino también sobre la capital de la nación Azteca.
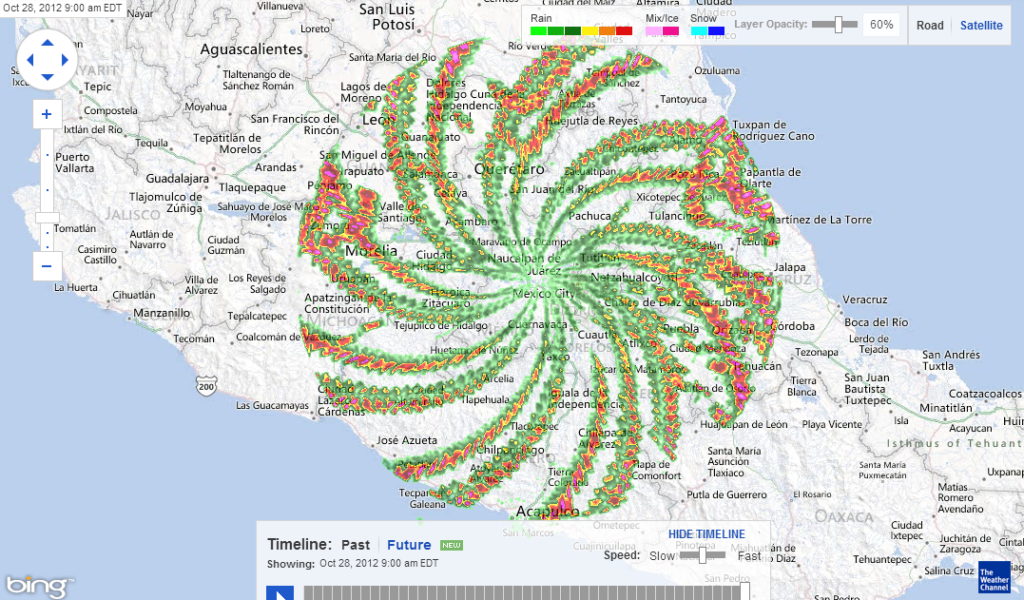
Otra anomalía de radar que apareció sobre México DF en diciembre de 2012. Gráficos: Cortesía/ The Weather Channel.
Recientemente, usuarios de las redes han logrado identificar fenómenos anómalos similares en otras partes del mundo; en lugares tan alejados como Australia y Rusia.
Por esta razón, el tema de las extrañas formas captadas a nivel mundial por los ecos de radar, se ha vuelto una verdadera sensación en internet. En el siguiente enlace podrán apreciar el archivo histórico de la “Anomalía de Guanajuato”; captado por el portal climático Ventusky.com
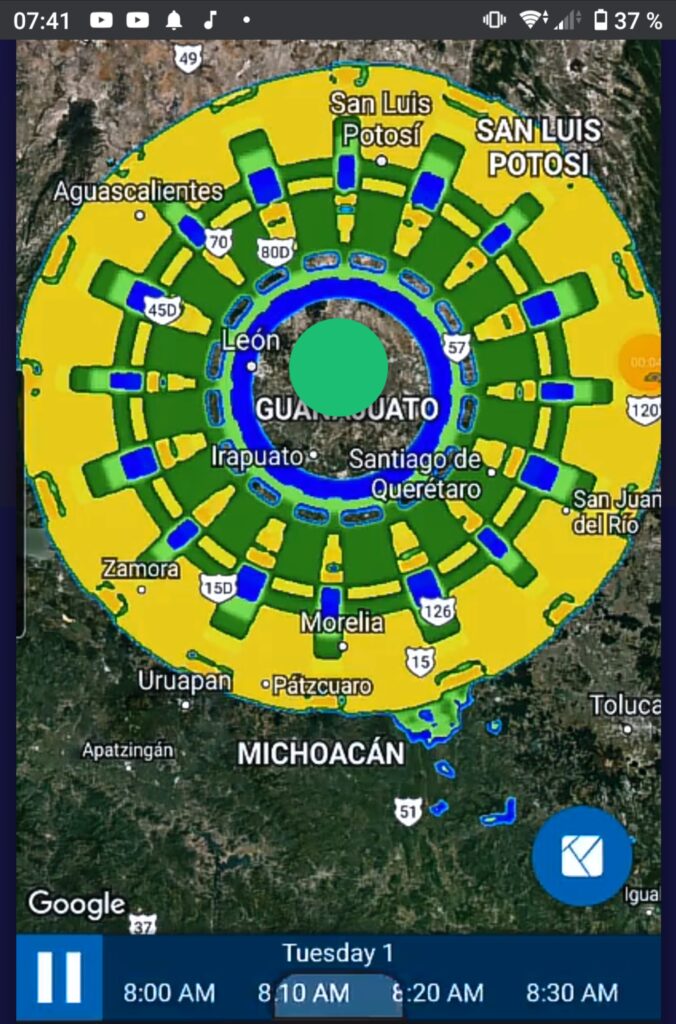
Captura de pantalla: Aplicación climática basada en los datos de satelites GOES donde también se muestra la anomalía. Gráfico: Cortesía/ forocoches.com
El conocido youtuber español Iván Martínez Juan, quien además es experto en informática y sistemas, ha realizado un interesante análisis de la anomalía de Guanajuato; donde expone diversas teorías que van desde avanzados sistemas de microondas, hasta la posible evidencia de vida extraterrestre que nos esté visitando.
A la hora de cierre de esta nota informativa, aún persisten mas preguntas que hipótesis de respuesta al extraño fenómeno captado por el sistema de radar doppler, tanto en los cielos mexicanos como en otras partes del planeta.
[Fuentes]: ACN | Windy.com | Ventusky.com | Open Weather | Redes
No dejes de leer: No dejes de leer: El Pentágono inicia audaz plan de desarrollo de satélites para la guerra espacial
* Infórmate al instante, únete a nuestro canal de Telegram NoticiasACN
Tecnología
LG Electronics presenta innovaciones en InfoComm 2025

En el marco de InfoComm 2025, la convención más relevante de la industria Pro AV en Norteamérica, LG Electronics adaptó un enfoque renovado que combina demostraciones inmersivas de productos, integraciones con socios estratégicos y reuniones consultivas.
El stand de la compañía en Orlando se transformó en un espacio de interacción bajo el lema “Conectar, Innovar y Elevar con LG”, donde se exhibieron las últimas tecnologías de visualización comercial.
Además, las soluciones de LG estuvieron presentes en más de 20 stands de socios, con aplicaciones en mercados verticales clave.
“Nuestra estrategia en InfoComm 2025 es comenzar o fortalecer las relaciones, introducir ideas de colaboración y luego seguir con consultas más profundas. Se trata de un enfoque más completo y centrado en el desarrollo de soluciones a la medida para los clientes”, afirmó David Bacher, responsable de marketing B2B de LG Electronics USA.
Entre los productos destacados se encuentran el LG CreateBoard de 75 pulgadas, el LG MAGNIT AM Micro LED de 136 pulgadas, la pantalla Ultra Stretch 21:9 de 105 pulgadas, el OLED Transparente de 55 pulgadas, las pantallas LG UH5N Series de 55 pulgadas, las Ultra Stretch de 37 pulgadas, los kioscos de 27 pulgadas y las soluciones LG Business Cloud.
Uno de los aspectos más llamativos del evento es la pantalla OLED transparente de 30 pulgadas con asistente de inteligencia artificial, desarrollada en colaboración con la empresa Invisible Arts.
Este dispositivo está diseñado para funcionar como un conserje digital o asistente virtual, capaz de optimizar procesos operativos y mejorar la experiencia del cliente mediante la interacción con un humano sintético.
LG también colabora con una red de socios que presentan soluciones integradas con tecnología de la marca, incluyendo pantallas All-in-One, monitores médicos y quirúrgicos, ordenadores portátiles ultraligeros, pantallas ultraelásticas y dispositivos de alto brillo para exteriores.
Para incentivar la participación, la compañía ha lanzado el juego LG Partner Pursuit, que invita a los asistentes a recorrer los stands de sus aliados y participar por premios.
“No hay mejor manera de demostrar el poder de nuestras soluciones que nuestros socios mostrándolas en acción”, concluyó Bacher.
“En InfoComm 2025, no nos limitamos a exponer: colaboramos, asesoramos y cocreamos con nuestros socios y clientes”.
Nota de prensa
Te invitamos a leer
McDonald’s Venezuela promueve competencias escolares en matemáticas y lengua
Infórmate al instante únete a nuestros canales
WhatsApp ACN – Telegram NoticiasACN – Instagram acn.web – TikTok _agenciacn – X agenciac
-

 Política19 horas ago
Política19 horas agoArmando Amengual oficializó su candidatura a la Alcaldía de Valencia en histórica unidad absoluta
-

 Economía17 horas ago
Economía17 horas agoMundo Fix reinauguró su sede en Valencia con planes de expansión nacional
-

 Economía17 horas ago
Economía17 horas agoMigurt presenta su sabor a durazno
-

 Economía16 horas ago
Economía16 horas agoPrecio del dólar para 2 de julio y de otras divisas extranjeras

























